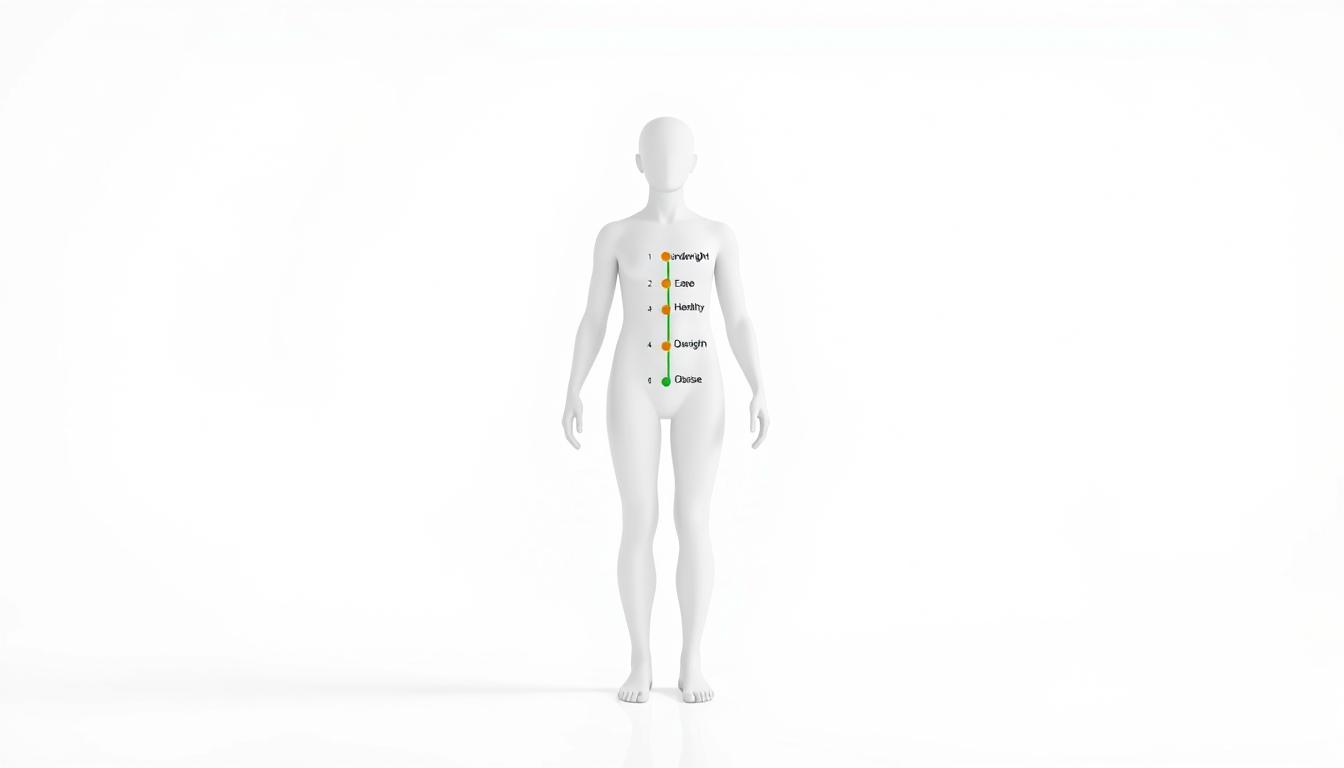
Do you know your ideal weight and why it’s so important for your health? Keeping an ideal body mass index can lower your risk of many health problems.
The CDC says a healthy BMI range for adults is 18.5 to 24.9. This tool helps doctors tell you how to manage your weight.
Knowing your healthy BMI range is the first step to a healthier life. It helps you check your health and make smart choices about food and exercise.
Key Takeaways
- Maintaining an ideal body mass index is crucial for overall health.
- The CDC defines a healthy BMI range as between 18.5 and 24.9 for adults.
- BMI is a tool used to categorize individuals into different weight categories.
- Understanding your BMI helps in making informed health decisions.
- A healthy BMI reduces the risk of various health issues.
Understanding BMI and Its Importance
BMI is key in health and fitness. It’s a starting point for many health checks. BMI, or Body Mass Index, shows how weight relates to height.
What is BMI?
BMI is found by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. This simple formula shows if a person’s weight is healthy for their height.
Why is BMI Relevant to Health?
BMI helps spot weight-related health risks. The Cleveland Clinic says BMI can show disease risks like diabetes and heart disease.
Keeping a healthy BMI can lower these risks. It improves health and wellbeing.
How is BMI Calculated?
BMI uses weight and height. The formula is: BMI = weight (in kg) / height (in meters)². For instance, a 70 kg person who is 1.75 meters tall has a BMI of 22.86.
| Height (meters) | Weight (kg) | BMI |
|---|---|---|
| 1.60 | 50 | 19.53 |
| 1.75 | 70 | 22.86 |
| 1.80 | 80 | 24.69 |
For more on BMI and its effects, check out Health Weight Calculator. They offer tips on losing weight and improving body composition for a healthy BMI.
Healthy BMI Range for Adults
The healthy BMI range for adults is key to knowing your nutritional health and risk of diseases. Keeping a BMI in the healthy range can lower the risk of diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and some cancers.
Ideal BMI Range
The ideal BMI for adults is between 18.5 and 24.9. This range is linked to the lowest health risks. A BMI in this range means you have a healthy weight, which is important for your overall health.
BMI Categories Explained
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) breaks down BMI into several categories. Knowing these categories can help adults understand their health status.
| BMI Category | BMI Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight | Less than 18.5 | Potential health risks due to low body weight. |
| Healthy Weight | 18.5 – 24.9 | Generally associated with lower risk of health problems. |
| Overweight | 25 – 29.9 | Increased risk of health issues such as diabetes and heart disease. |
| Obesity | 30 or greater | Higher risk of serious health conditions including certain cancers. |
Implications of Being Outside the Healthy Range
Being outside the healthy BMI range can lead to serious health problems. Adults who are underweight or overweight face higher risks. Being underweight can cause nutrient deficiencies and osteoporosis, while being overweight or obese raises the risk of diseases like hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
Knowing your BMI category and taking action can greatly improve your health.
BMI Guidelines for Children and Teens
It’s important to know BMI guidelines for kids and teens to help them grow healthy. Unlike adults, BMI for them takes into account their age and sex, not just weight and height.
BMI Calculations for Younger Populations
For kids and teens, BMI is figured out with special percentiles for age and sex. This way, it’s more accurate to see how they weigh compared to others. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has growth charts for kids and teens aged 2 to 20.
Understanding Percentiles
Percentiles help compare a child’s or teen’s BMI to others of the same age and sex. For example, a 50th percentile BMI means they’re average. Being below the 5th percentile means they’re underweight, and above the 95th percentile means they’re obese.
Health Risks Associated with Deviations
Being too thin or too heavy can signal health risks. Kids and teens who are underweight or overweight face dangers like diabetes, high blood pressure, and mental health issues.
| BMI Percentile Range | Weight Status | Potential Health Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 5th percentile | Underweight | Nutritional deficiencies, osteoporosis |
| 5th to 84th percentile | Normal weight | Lower risk of health problems |
| 85th to 94th percentile | Overweight | Increased risk of obesity-related health issues |
| 95th percentile or higher | Obese | High risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease |
By keeping an eye on BMI percentiles, parents and doctors can spot health risks early. This way, they can take steps to prevent them.
Factors Influencing BMI
BMI is not just one thing; it’s a mix of genetics, lifestyle, and environment. Knowing these factors helps us keep a healthy BMI.
Genetics and BMI
Genetics are a big part of BMI. Studies show they affect how our body handles fat. Genetic traits can make it harder to lose or gain weight. So, it’s key to think about genetics when looking at BMI.
Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact
What we eat and how active we are affects BMI a lot. Eating well and staying active keeps BMI healthy. But, being too sedentary can cause weight gain and health issues. The infographic below shows how lifestyle choices impact BMI.
Our diet and activity level directly affect our BMI. Making smart choices can help us reach and keep a healthy BMI.
Environmental Factors
Our environment, like where we live and what food is available, also plays a role in BMI. People in areas with few healthy options might struggle to stay healthy. Fixing these environmental issues is important for everyone’s health.
Understanding BMI’s many factors helps us see health in a bigger way. We should know our genetic side, make good lifestyle choices, and push for better environments for health.
Tips for Achieving a Healthy BMI
To keep a healthy BMI, you need to eat right, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. These steps help you reach and stay at a healthy weight. Here are the key tips and guidelines to follow.
Nutrition and Dietary Guidelines
Eating a balanced diet is key for a healthy BMI. You should eat a variety of foods like fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Try to avoid processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables: Aim for at least five servings a day.
- Choose whole grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread are rich in fiber and nutrients.
- Incorporate lean proteins: Foods like chicken, fish, beans, and lentils are excellent sources of protein.
- Limit processed foods: Try to avoid or limit foods that are high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
Exercise Recommendations
Regular exercise is also vital for a healthy BMI. It helps burn calories and build muscle, which aids in weight management. Aim for a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
| Exercise Type | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic Exercise | At least 150 minutes/week | Improves cardiovascular health, burns calories |
| Strength Training | 2-3 times/week | Builds muscle, boosts metabolism |
| Flexibility Exercises | 2-3 times/week | Enhances flexibility, reduces injury risk |
The Role of Sleep and Stress Management
Getting enough sleep and managing stress are crucial for a healthy BMI. Poor sleep can lead to weight gain, and stress can make you eat more.
Try meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to manage stress. Also, make sure to sleep 7-9 hours each night for better health and weight control.
Common Misconceptions About BMI
BMI is widely used, but it has many misconceptions. One big mistake is thinking BMI directly measures health. This is not true.
Body Composition vs. BMI
BMI is found by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. But it doesn’t tell the difference between muscle and fat. For example, athletes with lots of muscle might have a high BMI without being overweight.
It’s important to know the difference between BMI and body composition. Body composition analysis shows more about health. It measures body fat, muscle, and other health signs.
When BMI May Not Be Accurate
BMI might not show the right health picture in some cases. For example, it’s not right for:
- Athletes or people with a lot of muscle
- Older adults who might have lost muscle
- Pregnant women, as it doesn’t count the baby’s weight
In these cases, just using BMI can lead to wrong health risk ideas.
Alternative Tools for Measuring Health
To get a better health view, use other metrics with BMI. These include:
| Metric | Description | Health Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Waist Circumference | Measures fat around the waist | Risk of chronic diseases like diabetes |
| Body Fat Percentage | Directly measures body fat | Health risks from too much fat |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio | Compares waist to hip size | Risk of heart diseases |
Using these metrics with BMI helps calculate BMI better. It also helps understand health status better. Always talk to health experts for a full health check.
Knowing BMI’s limits and using it right helps keep a healthy lifestyle. It helps reach an ideal body mass index.
Conclusion: Maintaining a Healthy BMI
Keeping a healthy BMI is key for our overall health. We’ve looked into why BMI matters, how to calculate it, and guidelines for different ages. It’s important to know the healthy BMI range and follow the guidelines.
Informing Yourself
Staying up-to-date with health research and guidelines is crucial. We can do this by following trusted health organizations and talking to doctors.
Regular Health Checkups
Regular health checkups are important for tracking our BMI and health. These visits help doctors check our health and give us advice tailored to us.
Support Systems for Health Goals
Having support can really help us reach our health goals. Joining a community or finding a health buddy can give us the motivation and encouragement we need to stay healthy.