Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure to assess body fat based on height and weight.
For women, understanding BMI can provide valuable insights into health and potential risks.
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered healthy for most adult women, though this range may vary based on factors like age and ethnicity.
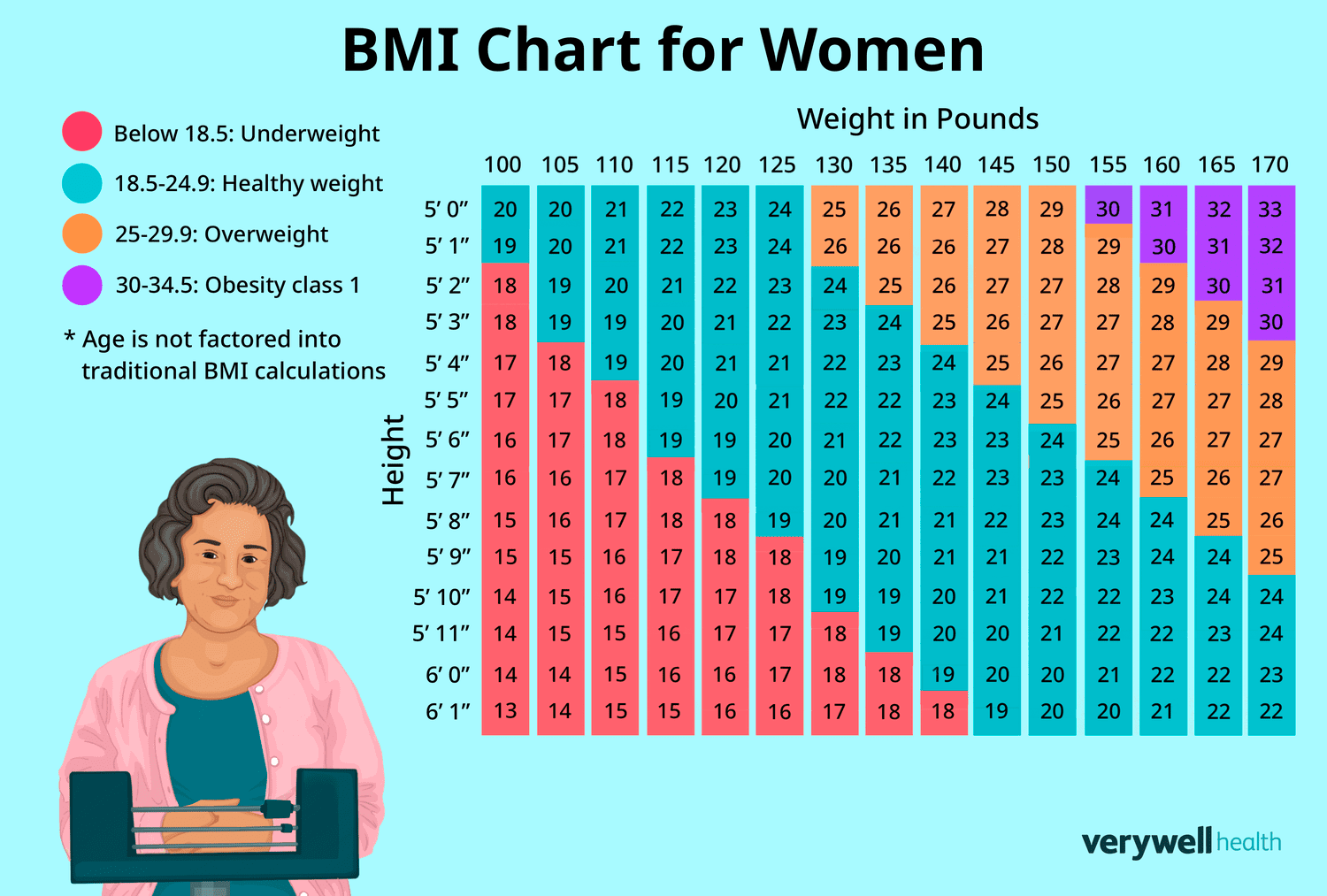
BMI charts for women offer a quick way to determine if one’s weight falls within a healthy range.
While BMI is a useful tool, it’s important to remember that it doesn’t account for muscle mass, bone density, or body composition.
This means that some women, particularly athletes or those with high muscle mass, may have a higher BMI without necessarily being overweight.
We’ll explore the nuances of BMI charts for women, including how to interpret the results and what factors to consider beyond the numbers.
By understanding BMI and its limitations, women can make more informed decisions about their health and wellness goals.
Key Takeaways
- BMI provides a general indication of body fat, but doesn’t account for individual factors
- Women’s healthy BMI ranges may vary based on age, ethnicity, and body composition
- Regular health check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers complement BMI assessments
Understanding BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a key measure used to assess body composition and health risks. It provides a simple way to estimate body fat based on height and weight.
Definition and Importance
BMI is a numerical value that helps classify people into weight categories. It’s used to screen for weight issues that may lead to health problems.
While BMI doesn’t directly measure body fat, it’s a useful starting point for evaluating overall health.
We use BMI because it’s easy to calculate and applies to most adults. It helps identify potential weight-related health risks, such as heart disease and diabetes.
However, BMI has limitations. It doesn’t account for muscle mass, bone density, or body composition.
Athletes or very muscular individuals may have a high BMI but low body fat.
BMI Calculation Method
To calculate BMI, we use a simple formula:
BMI = weight (kg) / height² (m²)
For those using pounds and inches:
BMI = (weight in pounds × 703) / height² (in inches)
BMI calculators are widely available online for quick results.
The resulting number falls into one of these categories:
- Underweight: Below 18.5
- Normal weight: 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9
- Obese: 30 or above
It’s important to note that BMI is just one tool. A healthcare provider should interpret results, considering factors like age, muscle mass, and overall health.
BMI Chart for Women
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a useful tool for assessing weight status in women. It provides a general indication of health risks associated with different body compositions.
Interpreting the BMI Chart
BMI charts for women use height and weight to calculate a numerical value. This value falls into one of several categories. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal weight for most adult women.
We interpret BMI values as follows:
- Underweight: BMI below 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25 to 29.9
- Obese: BMI 30 or higher
It’s important to note that BMI doesn’t measure body fat directly. Some women, like athletes, may have a high BMI due to muscle mass rather than excess fat.
BMI Ranges for Women
BMI ranges can vary slightly based on age and other factors. For most adult women, we use the following general guidelines:
| BMI Range | Weight Status |
|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal Weight |
| 25.0 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30.0 and above | Obese |
Postmenopausal women may have different BMI considerations due to changes in body composition. As women age, they typically lose muscle mass and gain fat, which can affect BMI interpretation.
We recommend using BMI as one of several tools to assess overall health. Other factors like waist circumference, body fat percentage, and lifestyle habits should also be considered for a comprehensive health evaluation.
Health Implications
A woman’s BMI can significantly impact her health. Different BMI ranges are linked to various health risks and outcomes. Let’s explore the potential effects of low and high BMIs on women’s well-being.
Risks of Low BMI
Women with a BMI below 18.5 may face several health challenges. These can include:
• Weakened immune system • Osteoporosis • Fertility issues • Anemia • Hormone imbalances
Low BMI can lead to malnutrition, causing hair loss and dry skin. It may also result in irregular menstrual cycles or amenorrhea. Women with very low BMI are at higher risk for complications during pregnancy.
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for proper organ function and overall vitality. We recommend consulting a healthcare provider if BMI falls below the healthy range.
Risks of High BMI
A BMI above 25 in women is associated with increased health risks. These may include:
• Type 2 diabetes • Heart disease • High blood pressure • Certain cancers (e.g., breast, colon) • Sleep apnea
Excess weight can put strain on joints, leading to osteoarthritis. It may also cause fertility problems and complications during pregnancy. Women with high BMI often experience decreased energy levels and mobility issues.
Losing weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce these risks. Even small reductions in BMI can lead to significant health improvements.
BMI and Overall Health
While BMI is a useful tool, it’s not the only measure of health. We consider other factors when assessing a woman’s overall well-being:
• Waist circumference • Body fat percentage • Muscle mass • Diet quality • Physical activity level
BMI doesn’t account for muscle mass, which can lead to misclassification in athletic women. It also doesn’t show where fat is stored in the body. Abdominal fat carries more health risks than fat in other areas.
Regular check-ups, balanced nutrition, and consistent exercise are key to maintaining good health. We encourage women to focus on these aspects rather than solely on BMI numbers.
Contextual Considerations
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a useful tool, but it’s not perfect. We need to look at other factors to get a full picture of a woman’s health. Age and muscle mass play big roles in how we interpret BMI results.
Age and BMI
As women get older, their bodies change. This affects how we use BMI charts.
Postmenopausal women often have less muscle mass. Even if they weigh less, they might have more body fat.
Younger women may have different BMI needs. Their bodies are still developing. We must be careful when judging their BMI.
For older women, a slightly higher BMI might be okay. It could even be good for their health. We should look at each woman’s overall health, not just her BMI number.
Muscle Mass vs. Fat Mass
BMI doesn’t tell us what’s muscle and what’s fat. This is a big issue for active women.
Highly active women and athletes often have more muscle. Muscle weighs more than fat.
A woman with lots of muscle might have a high BMI. But she could be very healthy. We need to look at body fat percentage too.
On the flip side, someone with a normal BMI might have too much fat. This is called “skinny fat.” It’s why we can’t rely on BMI alone.
We should use other methods like body fat tests. These give us a better idea of a woman’s health.
Frequently Asked Questions
BMI charts for women provide valuable health insights. They consider factors like age, height, and life stages to determine healthy weight ranges. Let’s explore some common questions about BMI for women.
How can a woman determine her ideal Body Mass Index?
Women can calculate their BMI using weight and height measurements. The formula is weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
For quick results, online calculators are available. These tools provide instant BMI values and corresponding weight categories.
At what BMI is a female considered to be in a healthy weight range?
A healthy BMI range for adult women is generally between 18.5 and 24.9. This range is associated with lower health risks.
It’s important to note that BMI is just one health indicator. Other factors like muscle mass and body composition also play a role.
What factors affect the BMI chart for women?
Several factors influence BMI charts for women. Muscle mass, age, and activity level can all impact BMI readings.
Highly active women or bodybuilders may have higher BMIs due to increased muscle mass. Postmenopausal women might see changes in their BMI as body composition shifts with age.
What is the significance of age in interpreting a woman’s BMI?
Age is crucial when interpreting BMI. As women age, their body composition naturally changes.
Older women may have higher body fat percentages even at lower weights. This means BMI might not always accurately reflect their health status.
How does height influence the calculation of BMI for women?
Height is a key component in BMI calculations. Taller women will have lower BMIs than shorter women of the same weight.
This is because BMI uses the square of height in its formula. It’s important to consider height when interpreting BMI results.
What is the impact of BMI on a woman’s health at different life stages?
BMI can affect women’s health differently throughout life. During pregnancy, BMI helps determine healthy weight gain.
In menopause, BMI changes may reflect shifts in hormone levels and metabolism.
Throughout adulthood, maintaining a healthy BMI can lower risks of certain health conditions.