Have you ever wondered why some people feel energized while others struggle with fatigue, even when following similar routines? The answer might lie in a critical yet often overlooked health indicator. Tracking this metric could unlock insights into your energy levels, recovery, and overall wellness.
Hydration isn’t just about drinking eight glasses daily. Every cell in our system relies on fluid balance to function. Adults typically maintain levels above 50% throughout life, but individual variations matter. This measurement reflects how efficiently nutrients move, joints stay cushioned, and temperature stays stable.
Our guide explores science-backed methods to evaluate this vital sign. From the Watson formula to bioelectrical impedance tools, we’ll break down practical ways to assess your status. You’ll learn why numbers matter more than thirst cues and how to spot imbalances early.
We’re here to simplify complex data into actionable steps. By the end, you’ll know how to connect these figures to daily habits and long-term wellness goals. Let’s dive into the details together.
Key Takeaways
- Hydration impacts energy, joint health, and nutrient delivery
- Adults maintain fluid levels above 50% for optimal function
- Multiple methods exist for accurate measurement
- Early imbalance detection prevents health complications
- Practical tools transform data into lifestyle adjustments
Understanding Body Water Percentage and Its Importance
Did you know your body’s fluid balance acts like a silent health manager? This measurement shows how much of your weight comes from fluids rather than bones, muscles, or fat. Adults typically carry about 60% of their mass in fluids, though this shifts with lifestyle and biology.
What Is Body Water Percentage?
Think of it as your internal moisture meter. The total body water includes fluids inside cells and surrounding them. Newborns start at 75% fluid content, while older adults may dip below 50%. Muscle holds more moisture than fat, explaining why athletes often show higher percentages.
Why Hydration Is Essential for Health
Fluids power every cellular process. They transport nutrients, cushion joints, and regulate heat. Research shows even 2% dehydration reduces focus and physical performance. Proper levels support kidney function and skin elasticity while aiding digestion.
| Age Group | Healthy Range | Key Influencers |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0-1 year) | 70-75% | Rapid growth phase |
| Adult Men | 55-65% | Muscle mass, activity level |
| Adult Women | 50-60% | Body fat distribution |
| Seniors (65+) | 45-55% | Kidney efficiency, medication use |
Maintaining your personal sweet spot helps prevent headaches, fatigue, and long-term health risks. Track changes during illness or intense training when needs spike. Simple adjustments in fluid intake can restore balance before minor dips become major issues.
How to interpret body water percentage
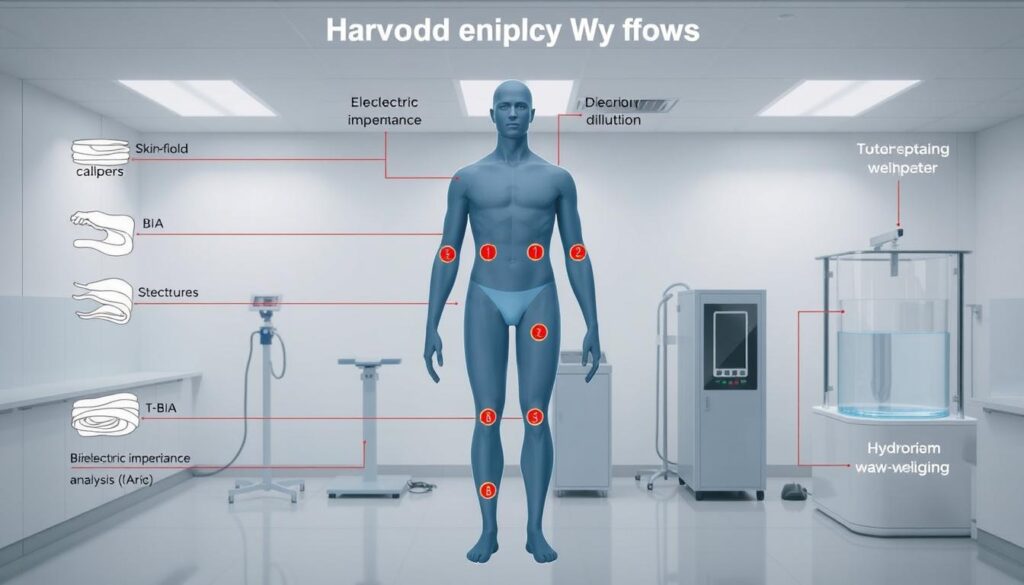
What if your scale could reveal more than just weight? Modern health tracking now quantifies what’s beneath the surface. Three primary approaches gauge fluid balance: clinical methods, mathematical models, and consumer tech.
Methods for Measuring Body Water Levels
Hospitals often use isotope dilution or hydrometry for precision. These gold-standard tests track marked water molecules through blood samples. For daily use, bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) devices send safe electrical currents to estimate resistance in tissues.
Smart scales combine BIA with weight data. While less accurate than lab tests, they track trends effectively. One study found BIA devices within 3% of clinical results for most adults.
Using the Watson Formula for Accuracy
Developed in 1980, this equation calculates total body water (TBW) using height centimeters and weight kilograms. Men and women have different formulas:
- Men: 2.447 – (0.09156 × age) + (0.1074 × height) + (0.3362 × weight)
- Women: -2.097 + (0.1069 × height) + (0.2466 × weight)
Multiply your result by 0.93 (men) or 0.83 (women) for plasma volume adjustment. Divide TBW by total body weight to get your percentage. Athletes often show higher values due to muscle’s water-rich nature.
Research in the Journal of Applied Physiology confirms this method’s reliability for population studies. Pair it with smart devices for personalized insights.
Body Water Percentage Through Different Life Stages
Our fluid composition evolves dramatically from cradle to golden years. This natural progression reflects shifting biological needs and body composition changes.
Early Development: The First 18 Years
Newborns begin life as hydration powerhouses, with 75-78% fluid content. This high range supports rapid cell growth and temperature regulation. By age one, percentages typically drop to 65% as body fat increases.
Children maintain 60-65% until puberty. Hormonal changes during adolescence alter muscle-to-fat ratios, creating gender-based differences. Teen boys often retain slightly more fluids than girls due to developing lean mass.
Adult Shifts and Special Conditions
After 30, most people lose about 0.5% fluid content per decade. Muscle mass decline and fat accumulation drive this change. Seniors face additional challenges:
- Reduced kidney efficiency
- Medication side effects
- Decreased thirst signals
| Life Stage | Average Range | Key Influences |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0-1) | 65-75% | Growth rate, feeding method |
| Children (1-12) | 60-65% | Activity level, nutrition |
| Pregnancy | +2-3% baseline | Blood volume expansion, fetal needs |
| Seniors (65+) | 45-55% | Organ function, mobility |
Expectant mothers require extra fluids for amniotic fluid and increased blood volume. Monitoring becomes crucial when morning sickness or swelling occurs. Simple adjustments like electrolyte-rich snacks help maintain balance during these transitions.
Hydration, Health Benefits, and Associated Risks
What keeps your brain sharp and joints moving smoothly? The answer flows through every cell. Balanced fluid levels act as your body’s natural maintenance crew, supporting critical functions while preventing system failures.
Key Benefits of Proper Hydration
Optimal fluid balance powers mental clarity and physical performance. Studies show hydrated individuals solve problems 14% faster and maintain better focus during tasks. Joints stay lubricated, reducing stiffness during movement.
Water acts as your cardiovascular partner, helping maintain healthy blood pressure by supporting plasma volume. It also flushes waste through kidneys and sweat. Even mild deficits impair temperature control, making you vulnerable to heat stress during activity.
Recognizing Signs of Dehydration and Overhydration
Dark urine, fatigue, and dizziness signal fluid shortages. Research reveals that losing just 1-2% of body weight in water reduces endurance and reaction times. Chronic dehydration strains kidneys and increases stone formation risks.
Conversely, excessive intake dilutes sodium levels, causing water intoxication. Symptoms include nausea, headaches, and confusion. A tracking tools study found marathon runners who overhydrated developed hyponatremia 13% more often than those following thirst cues.
“Balance matters more than extremes—listen to your body’s signals before reaching for another bottle.”
Most adults need 9-13 cups daily, but needs spike with exercise or high temperatures. Pair water with electrolyte-rich foods during prolonged activity to maintain equilibrium.
Managing Your Daily Water Intake
Hydration thrives on personalized strategies. We all need fluid, but the right amount depends on our unique biology and routines. Let’s explore practical ways to align intake with your daily rhythm.
Tailored Fluid Guidelines
Start with baseline needs: 0.5-0.6 ounces per pound of body weight. A 150-pound person needs 75-90 ounces daily. Adjust using this framework:
| Lifestyle Factor | Adjustment | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Exercise | +12 oz per 30 mins | Post-run electrolyte drink |
| Heat/Humidity | +20-30% baseline | Carry insulated bottle |
| High Altitude | +1.5x baseline | Mountain hiking prep |
Active individuals lose fluids faster through sweat. Drink 16 oz two hours before workouts, then 4-6 oz every 15 minutes during. Pair with salty snacks if sweating heavily.
Busy days demand smart hydration hacks. Set phone reminders or mark bottles with time-based goals. Herbal teas and water-rich foods like cucumbers count toward your total.
Signals and Solutions
Urine color remains the simplest check—aim for pale lemonade hues. Dry skin and midday slumps often signal shortages. Proper hydration supports cell repair and helps regulate blood pressure by maintaining plasma volume.
Did you know adequate fluids assist fat metabolism? Studies show drinking 17 oz boosts metabolic rate by 30% for 40 minutes. Use our body water calculator for personalized recommendations based on your stats.
Remember: consistency beats perfection. Small sips throughout the day work better than gulping large amounts at once. Share goals with friends or coworkers to build accountability—health thrives in community.
Monitoring Your Body Composition Effectively
Modern health tracking has moved beyond basic metrics to reveal cellular-level insights. Advanced tools now map fluid distribution alongside muscle and fat ratios. This data helps optimize hydration strategies and identify hidden imbalances.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Explained
BIA devices send low-level electrical currents through tissues. Fluids conduct this signal faster than fat or bone, creating precise resistance measurements. Studies show these readings correlate with clinical hydration assessments 85% of the time.
Traditional methods like urine tests only show short-term status. BIA tracks total body fluid shifts over weeks, revealing patterns. Athletes use this data to time electrolyte intake, while seniors monitor kidney-related changes.
Smart Scale Advantages
Home devices sync with apps to visualize trends in muscle mass and hydration levels. Morning weigh-ins provide consistent readings—key for accuracy. Look for scales measuring multiple frequencies (5kHz-100kHz) to assess different tissue depths.
Regular tracking helps spot brain fluid retention or kidney-related imbalances early. One trial found users improved hydration habits 40% faster with visual progress charts. Pair measurements with symptom logs for complete insights.
While lab tests remain gold-standard, smart tools empower daily decisions. Consistent monitoring creates actionable health narratives—not just numbers. Your body composition story starts with reliable data collection.
Conclusion
Your hydration status acts as a silent partner in daily wellness. We’ve explored how total body water impacts nutrient delivery, joint health, and cellular repair. From clinical-grade analysis to smart home devices, multiple tools help track this vital metric.
The Watson formula and bioelectrical impedance methods offer practical ways to assess fluid balance. These strategies reveal patterns that simple weight measurements miss. Regular monitoring helps maintain levels within your ideal range, supporting every cell and biological process.
Optimal hydration isn’t about rigid rules—it’s about personalized adjustments. Pair intake with activity levels, climate, and life stage needs. Small habit changes, like using tracking apps or electrolyte-rich snacks, create lasting benefits.
Remember: your total body thrives when fluids stay balanced. Start with one actionable step this week—whether recalculating your needs or testing a BIA scale. Consistent attention to this metric builds resilience across every part of your system.