Are you curious about your weight status and its impact on your health? An underweight overweight calculator can provide valuable insights.
This tool, also known as a Body Mass Index (BMI) calculator, helps assess if a person’s weight falls within a healthy range.
While it’s not perfect, BMI serves as a useful starting point for evaluating overall health risks related to body weight.
It’s quick, easy, and widely used by healthcare professionals.
Using an underweight overweight calculator can motivate people to make positive lifestyle changes. It can also help identify potential health risks associated with being outside the healthy weight range.
Remember, BMI is just one piece of the health puzzle, and other factors should be considered for a complete picture.
Key Takeaways
- BMI calculators offer a simple way to assess weight status
- Being underweight or overweight can impact overall health
- Regular BMI checks can help track progress towards health goals
Understanding BMI and Its Importance
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a key tool for assessing body composition and health risks. It uses a simple calculation based on height and weight to estimate body fat levels.
BMI helps doctors and individuals gauge if a person’s weight falls within a healthy range.
What Is BMI?
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It’s a measure of body fat based on height and weight.
The BMI formula divides a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. For example:
BMI = weight (kg) / (height (m))²
A BMI calculator makes this math easy. People can quickly find out their BMI by entering their height and weight into an online tool.
BMI works for most adults. But it has limits. It doesn’t account for muscle mass or body shape.
Athletes or very muscular people may have a high BMI even with low body fat.
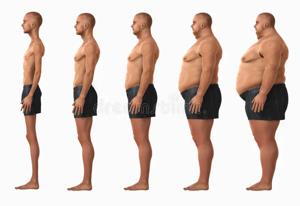
BMI Categories and Ranges
BMI values fall into different categories. These categories help identify potential health risks linked to weight. The main BMI ranges for adults are:
- Underweight: Below 18.5
- Normal weight: 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9
- Obese: 30 or higher
Some experts use more detailed categories for obesity. They may split it into Class 1, 2, and 3 based on higher BMI values.
BMI Prime is another way to look at BMI. It compares a person’s BMI to the upper limit of the normal BMI range (25). A BMI Prime of 1.0 means the person is at this upper limit.
The Relevance of BMI in Health Assessment
BMI is an important health indicator. It helps spot potential weight-related health issues.
A high BMI can point to higher risks of conditions like:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain cancers
A very low BMI can also signal health problems. It might mean malnutrition or other medical issues.
But BMI isn’t perfect. It doesn’t tell the whole story of a person’s health.
Doctors use BMI with other factors. These include diet, exercise habits, and family history. Together, they give a fuller picture of someone’s health status.
Health Risks Associated with BMI Extremes
BMI extremes can lead to serious health problems. Both being underweight and overweight carry risks that can impact a person’s quality of life and longevity.
Risks of Being Underweight
Being underweight can cause several health issues. People with low BMI may experience:
- Malnutrition: Not getting enough nutrients can weaken the immune system.
- Osteoporosis: Low body weight increases the risk of bone loss.
- Fertility problems: Women may have irregular periods or difficulty getting pregnant.
- Anemia: Low iron levels can lead to fatigue and weakness.
Underweight individuals often feel cold and tired. They may also have slow wound healing and hair loss. In severe cases, being underweight can lead to heart problems and organ failure.
Consequences of Overweight and Obesity
Overweight and obesity can cause many health problems. These include:
- Heart disease: Excess weight strains the heart and blood vessels.
- High blood pressure: Extra fat tissue needs more blood supply.
- Type II diabetes: Obesity can cause insulin resistance.
- Stroke: Overweight people have a higher risk of blood clots.
- Osteoarthritis: Extra weight puts stress on joints.
- Sleep apnea: Excess fat can block airways during sleep.
- Certain cancers: Obesity is linked to higher cancer risk.
Overweight people may also develop gallstones. Obesity can make daily activities harder and reduce life expectancy. Losing weight can lower these health risks and improve quality of life.
BMI Considerations for Specific Groups
BMI calculations need adjustments for different age groups and body types. Factors like growth patterns, aging, and muscle mass can affect BMI interpretation.
Children and BMI-for-Age
For kids, doctors use BMI-for-age percentiles. This method compares a child’s BMI to others of the same age and sex.
BMI-for-age takes into account that children’s bodies change as they grow. A normal BMI for a 5-year-old differs from that of a 15-year-old.
Weight classifications for children:
- Underweight: Below 5th percentile
- Normal weight: 5th to 85th percentile
- Overweight: 85th to 95th percentile
- Obese: Above 95th percentile
Doctors track BMI changes over time to spot potential health issues early.
Adult BMI and Age-Related Changes
As people age, their body composition shifts. Older adults often lose muscle mass and gain fat, even if their weight stays the same.
The adult BMI calculator works best for adults 20 to 65 years old. For older adults, BMI might not give a full picture of health risks.
Other factors to consider with age:
- Bone density changes
- Height loss
- Fat distribution shifts
Healthcare providers may use additional tests like waist circumference or body fat percentage for a more accurate assessment.
BMI in Athletes with High Muscle Mass
Athletes and bodybuilders often have high BMIs due to increased muscle mass. Muscle weighs more than fat, which can skew BMI results.
For these individuals, BMI might incorrectly classify them as overweight or obese. A football player and a person with a sedentary lifestyle might have the same BMI but very different body compositions.
Alternative methods for athletes:
- Body fat percentage measurements
- Skinfold caliper tests
- Hydrostatic weighing
These tests can provide a more accurate picture of an athlete’s health and fitness level than BMI alone.
Practical Guide to Measuring and Interpreting BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a useful tool for assessing weight status. It helps people understand their body composition and potential health risks.
How to Calculate BMI Accurately
To calculate BMI, divide weight by height squared. For metric units, use kilograms and meters. For US units, use pounds and inches, then multiply by 703.
Metric formula: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)² US formula: BMI = 703 x weight (lbs) / height (in)²
For accuracy:
- Measure height without shoes
- Weigh yourself in light clothing
- Use a reliable scale and measuring tape
Online BMI calculators make the process quick and easy. The CDC offers a user-friendly BMI calculator for adults.
Interpreting Your BMI Results
BMI categories for adults:
- Underweight: Below 18.5
- Normal weight: 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9
- Obese: 30 or higher
These ranges apply to most adults. BMI does not directly measure body fat. It may overestimate body fat in athletes or underestimate it in older adults.
A high BMI can indicate increased risk for conditions like type 2 diabetes, breathing problems, and heart disease. Low BMI may signal nutritional deficiencies or other health issues.
BMI is just one health indicator. Other factors like diet, exercise, and family history also affect overall health.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- BMI is below 18.5 or above 30
- BMI changes significantly in a short time
- You have concerns about your weight or body composition
A doctor can:
- Assess other health markers (blood pressure, cholesterol)
- Screen for weight-related conditions
- Provide personalized advice on diet and exercise
- Recommend specialist care if needed
Remember, BMI is a screening tool, not a diagnostic test. Only a healthcare professional can fully evaluate your health status and risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
BMI calculations help determine healthy weight ranges. Age, gender, and height are key factors in assessing if someone is underweight or overweight.
How is Body Mass Index (BMI) calculated?
BMI is found by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. The CDC offers BMI calculators to make this process easy.
For those who prefer imperial units, divide weight in pounds by height in inches squared. Then multiply by 703.
What BMI values correspond to being underweight or overweight?
A BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is normal weight.
A BMI of 25 to 29.9 indicates overweight. A BMI of 30 or higher is obese.
What factors are considered when using a BMI calculator for females?
Female BMI calculators often account for age and frame size. They may also consider body fat percentage.
Some calculators ask about pregnancy or breastfeeding status. These factors can affect weight and BMI results.
How does age affect BMI calculations?
BMI calculations differ for adults and children. Adult BMI calculators are for those 20 and older.
For children and teens, BMI is compared to others of the same age and sex. This creates percentiles to determine weight status.
What is the typical weight range for a specific height?
Weight ranges vary based on frame size and muscle mass. For a 5’6″ adult, a healthy weight is often between 115-154 pounds.
BMI calculators can provide more specific ranges based on individual height and weight.
At what point is a certain weight considered underweight for adolescents?
For adolescents, underweight is defined as a BMI below the 5th percentile for age and sex.
This means the child weighs less than 95% of others their age and sex.
A doctor should evaluate any concerns about adolescent weight.